Generation of FM Waves
Frequency Modulation (FM) waves can be generated using several different methods, including:
1. Direct FM Modulation: In this method, the carrier frequency is directly modulated by the modulating signal using a frequency modulator. The modulator changes the frequency of the carrier in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal.
2. Indirect FM Modulation: In this method, the carrier frequency is first phase modulated by the modulating signal, and then the phase-modulated signal is passed through a frequency discriminator, which produces an FM wave at the output.
3. Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Modulation: In this method, a PLL is used to generate an FM wave by controlling the frequency of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) using a feedback loop. The VCO frequency is modulated by the input signal, and the output of the VCO is passed through a frequency multiplier to produce the final FM signal.
4. Varactor Diode Modulation: In this method, a varactor diode is used as a voltage-controlled capacitor to modulate the resonant frequency of a LC oscillator circuit. The varactor diode capacitance is varied by a modulating signal, which changes the resonant frequency of the oscillator, producing an FM wave at the output.
5. Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) Modulation: In this method, a digital signal processor (DSP) is used to generate an FM signal by controlling the frequency of a digital oscillator. The DSP modulates the frequency of the oscillator in response to the input signal, and the output of the oscillator is passed through a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to produce the final FM signal.
Overall, the choice of FM wave generation method depends on factors such as the desired frequency range, modulation depth, and accuracy, as well as the available hardware and circuitry.
Indirect Method (Armstrong Method) of FM Generation
In this method, narrow-band FM wave is generated first by using phase modulator and then the wideband FM with desired frequency deviation is obtained by using frequency multipliers.
The above eq is the expression for narrow band FM wave In this case
The narrowband FM has some distortion due to the approximation made in deriving the expression of narrowband FM from the general expression. This produces some amplitude modulation in the narrowband FM which is removed by using a limiter in frequency multiplier.
Direct Method of FM Generation
In this method, the instantaneous frequency ƒ(t) of the carrier signal c(t) is varied directly with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal n(t). For this, an oscillator is used in which any one of the reactive components (either C or L) of the resonant network of the oscillator is varied linearly with n(t). We can use a varactor diode or a varicap as a voltagevariable capacitor whose capacitance solely depends on the reverse-bias voltage applied across it. To vary such capacitance linearly with n(t), we have to reverse-bias the diode by the fixed DC voltage and operate within a small linear portion of the capacitance-voltage characteristic curve. The unmodulated fixed capacitance C0 is linearly varied by n(t) such that the resultant capacitance becomes
C(t) = C0 − kn(t)
where the constant k is the sensitivity of the varactor diode (measured in capacitance per volt).
 |
| Hartley oscillator for FM generation |
The above figure shows the simplified diagram of the Hartley oscillator in which is implemented the above discussed scheme. The frequency of oscillation for such an oscillator is given
is the frequency sensitivity of the modulator. The Eq. (5.42) is the required expression for the instantaneous frequency of an FM wave. In this way, we can generate an FM wave by direct method.
Direct FM may be generated also by a device in which the inductance of the resonant
circuit is linearly varied by a modulating signal n(t); in this case the modulating signal being the current.
The main advantage of the direct method is that it produces sufficiently high
frequency deviation, thus requiring little frequency multiplication. But, it has poor frequency stability. A feedback scheme is used to stabilize the frequency in which the output frequency is compared with the constant frequency generated by highly stable crystal oscillator and the error signal is feedback to stabilize the frequency.


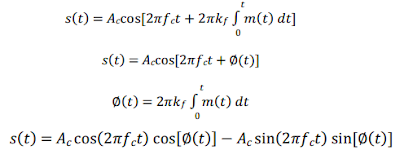



0 Comments
Do leave your comment